
|

|

|

|

|
SAPINDACEAE - - Soapberry Family

|

|

|

|

|
Black Maple (Acer nigrum) is a medium to large tree to 82 feet, rarely taller, with an open, flat to round-topped crown; trunk straight, to 3.9 feet in diameter. The National Champion has a circumference of 18.42 feet and a height of 70 feet. I assume, the common and scientific name, is in reference to the bark which is reportedly darker than A. saccharum, but any of the four species of "sugar maples" can have black bark, if beset by woodpeckers in the spring (see discussion under A. floridanum). The species name for this tree, "nigrum," means black.
The leaves** of black maple are reportedly deeper green on the upper surface than the other three "sugar maples," and the bark is also supposed to be darker. The leaves on this species are generally more likely to be 3-lobed, rather than 5-lobed as is the norm for the other three species. More importantly, the leaf blades on fruiting branches are rotund to subreniform, deeply cordate with narrow or closed sinus, mostly 3 (rarely 5)-lobed. Whether 3 or 5-lobed the leaf lobes are usually wider with a more abruptly narrowed tip than the other three "sugar maples." A. nigrum leaves, like A. leucoderme have the characteristic of drooping or curling on the edges (best observed with sun-exposed material). A. saccharum and A. barbatum leaves are relatively flat. The young branchlets of black maple are orange-tinged. And, compared with chalk maple, this species is generally a much larger, single-trunked tree.
**see the Leaf Comparison Chart on the Acer saccharum page
Riverbanks, streambanks, cove forests, river slope forests, especially over calcareous rocks. Found primarily west of the Appalachians.
Habitat information from:
Weakley, Alan S., Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States, Working Draft of 21 May 2015.
Black maple is found from southern Canada south to NY, NJ, through the Appalachians to NC, west to TN and extreme nw AR, north to southern MN and WI. And, despite the featured range map, Black Maple has been reported from four north Alabama counties, and one extreme northwest Georgia county (Dade).
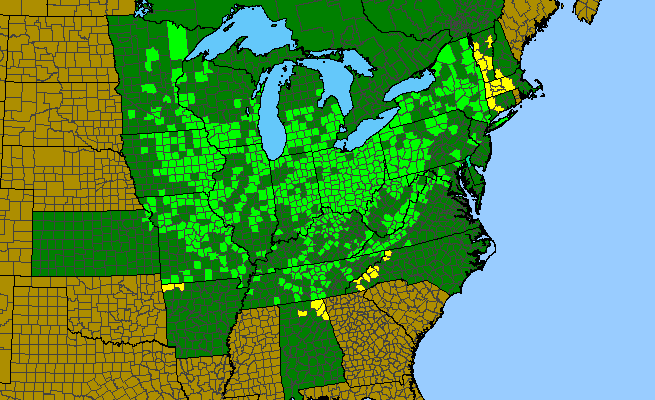
The native range of Acer nigrum (Black Maple)
Kartesz, J.T., The Biota of North America Program (BONAP). 2015. North American Plant Atlas. (http://bonap.net/napa). Chapel Hill, N.C. [maps generated from Kartesz, J.T. 2015. Floristic Synthesis of North America, Version 1.0. Biota of North America Program (BONAP). (in press)].
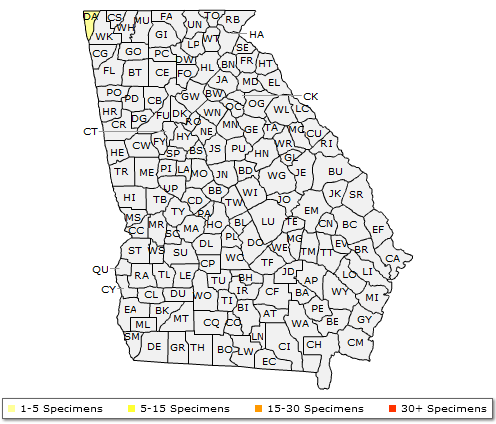
The Georgia range of Acer nigrum (Black Maple)
Zomlefer, W.B., J.R. Carter, & D.E. Giannasi. 2014 (and ongoing). The Atlas of Georgia Plants. University of Georgia Herbarium (Athens, Georgia) and Valdosta State University Herbarium (Valdosta, Georgia). Available at: http://www.georgiaherbaria.org/.
Guide to the Trees of North Georgia and Adjacent States
Web Page © Richard Ware
send Richard an E-mail